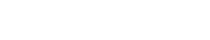Aerospace Blades
Precision Forging, Casting, Machining, Wax Molds, Blade Assembly
Aircraft engines are highly complex and precision thermodynamic machines that serve as the primary power source for aircraft. They are hailed as the "heart" of an airplane and regarded as the "jewel" of industrial manufacturing. Aerospace blades, which are among the engine’s core components, play a critical role in ensuring the safety and performance of engine systems. Their shape and manufacturing precision have a significant impact on the engine's power output. However, producing large quantities of blades that meet design specifications requires precise evaluation and analysis of inspection data, making this a vital step in the blade manufacturing process.
Steam Turbine Blades
Turbine blades are the core high-temperature components of gas turbines. Their development and manufacturing reflects a nation's industrial scale and technological expertise. As critical components for aerodynamic energy conversion, the dimensional accuracy of turbine blades not only determines whether the gas turbine can be assembled successfully but also ensures its safe and reliable operation.
Hydraulic Turbines
In hydropower stations, hydraulic turbines are among the most critical electromechanical devices, serving as the primary equipment for ensuring project functionality and efficiency. The normal operation and efficiency of hydraulic turbines directly impact the entire project. During operation, damage such as cavitation erosion, wear, deformation, cracking, and fragmentation can significantly reduce turbine efficiency and safety. To prevent these issues, precise measurement of blades during production is essential.
Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) can precisely inspect blade profiles and hole positions. The measurement data helps guide blade repair processes, assess repair quality, and ensure the turbines operates efficiently and reliably.
Impellers
Integral impellers, as critical components of power machinery, are widely used in aerospace and other industries. Key inspection areas include blade surfaces, flow channels, and leading edges. Inspection parameters cover blade profile tolerance, thickness, accuracy of the tip and inner flow channel contours, and precision of the leading edge profile.
1. Challenges in Impeller Blade Inspection: AEH’s 4-axis scanning system effectively handles the complex, twisted surfaces of impeller blades.
2. Measurement Software: Automatically calculates the rotary table angles for each measurement point, as well as safe probe entry and exit positions based on the theoretical blade geometry and twist clearance - significantly reducing programming time.
Blade Inspection
Measurement can be performed using non-contact point lasers, contact-trigger probes, or scanning probes.

Specialized blade software automatically launches measurement programs based on the blade type and generates inspection reports upon completion.
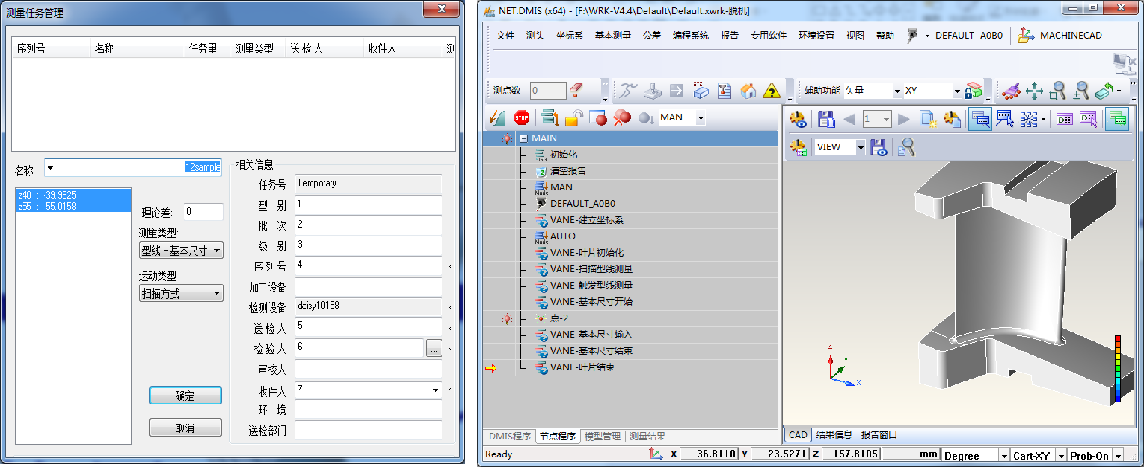
Coordinate systems can be established using various methods - such as point-line-plane alignment, RPS alignment, or three-center-point alignment - tailored to customer requirements.
When blade assembly references have regular surfaces, the point-line-plane alignment method is typically used. First, a rough coordinate system is established manually, followed by an automated fine alignment. Adjustments such as rotation and translation can be applied to refine the coordinate system.
When assembly references are irregular (e.g., cylindrical or serrated surfaces), RPS alignment is employed. Theoretical RPS points are used within a programmed loop to precisely establish the coordinate system.
Measurement Methods
Contact Scanning- Optical Rapid Multi-Axis Measurement Systems
Blade quality is critical to the performance of blade-integrated products. Traditional inspection methods, such as template checks and pneumatic gauges, have been largely replaced by coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), significantly enhancing both efficiency and accuracy. However, CMMs require a constant-temperature environment and have limited sampling speeds.
Beyond traditional contact and scanning CMMs, the AEH Optical Rapid Multi-Axis Measurement System provides a tailored solution for blade inspection. It integrates four-axis motion with white-light measurement, overcoming the limitations of contact probes and introducing a hybrid non-contact/rotary table measurement mode.
Blade Evaluation Software Features
1. Compatible with measurement devices from AEH, Hexagon, Zeiss, etc., automatically capturing blade data.
2. Processes data from triggers, scanners, lasers, and optical sensors.
3. Meets evaluation requirements for blades produced via precision forging, machining, casting, and more.
4. Offers diverse blade surface fitting methods, including:
· Pressure side (PS) / suction side (SS) global fitting
· PS-based fitting
· SS fitting
· Leading/trailing edge fitting
· Midline fitting
5. Provides tolerance evaluation options: uniform, segmented, or unilateral tolerances.
6. Customizable development tailored to unique customer needs.
Evaluation Parameters
Thickness: Maximum profile thickness, leading/trailing edge thickness.
Length: Chord length, X/Y-axis projected lengths.
Position: Leading/trailing edge positions.
Angle: Chord angle.
Profile per section: After best-fit alignment, highest and lowest points on PS/SS of each section, as well as the overall contour of each section.